1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

iuyi
hello搬运于
2025-08-24 22:40:40,当前版本为作者最后更新于2024-05-19 14:32:50,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
样例 #2
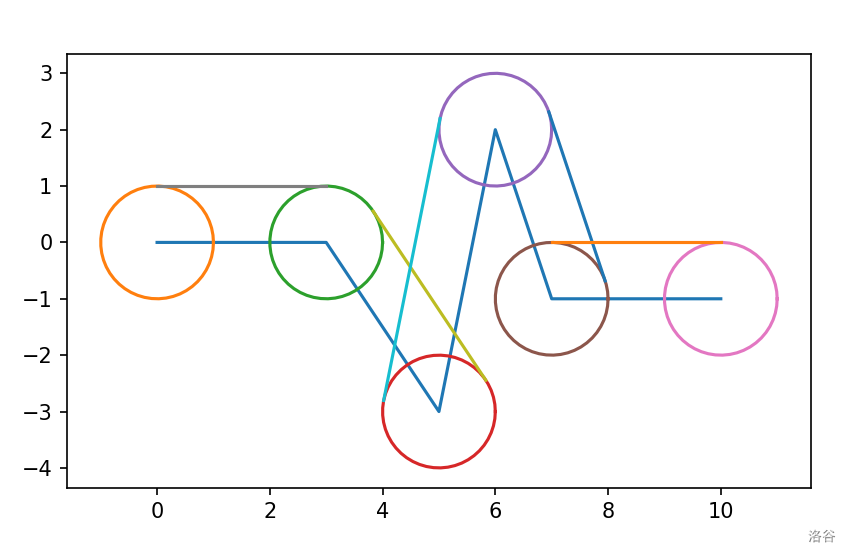
观察样例发现要求的曲线长度就是上图的上边界长度。具体来说图形包括每一段路沿法线方向平移 后得到的线段和所有以端点为圆心半径为 的圆。
首先想到的是沿着路径模拟。注意到并不是每一段路都有机会和车轮相切(比如说有一个宽度比车轮小很多的深坑),也就是说我们不能仅仅处理相邻两段的交点。我们还会发现路径上的圆弧不仅可以和相邻的线段相接,还可以和不相邻的线段(比如下面这组数据)或其他圆相接。
5 1.00 0.00 0.00 3.00 0.00 4.00 -3.00 5.00 2.00 7.00 2.00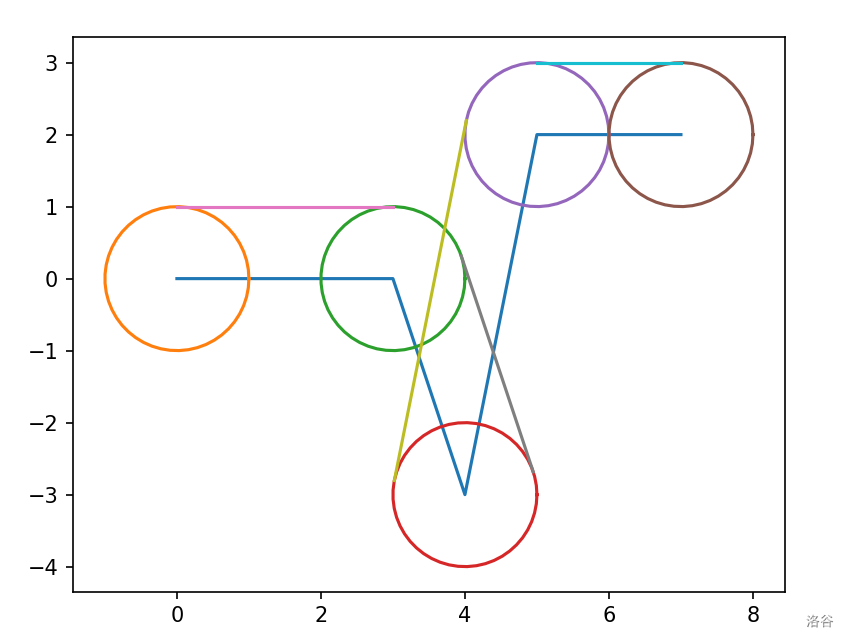
直接模拟需要处理几种不同类型的交点,看起来有点复杂,于是我们考虑一种类似于辛普森积分的做法。对于一个区间,如果当前区间的估计值和左右子区间的估计值之和误差很小就直接返回,否则就递归下去。
计算一个区间的曲线长度时取左右端点和中间点,将过这三点的圆弧(或线段)的长度作为近似值。由于上边界是由圆弧和线段构成的,所以这样算出的近似值在大部分的位置都是准确值。
import sys from cmath import phase, pi from math import sqrt import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np eps = 1e-8 # sys.stdin = open('1.in', 'r') n, r = input().split() n, r = int(n), float(r) road = [complex(*map(float, input().split())) for _ in range(n)] vec = [b - a for a, b in zip(road[:-1], road[1:])] norm = [v / abs(v) * 1j * r for v in vec] seg = [(a + n, b + n) for a, b, n in zip(road[:-1], road[1:], norm)] fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set_aspect(1) plt.plot([x.real for x in road], [x.imag for x in road]) for o in road: args = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi) plt.plot(o.real + r * np.cos(args), o.imag + r * np.sin(args)) for a, b in seg: plt.plot([a.real, b.real], [a.imag, b.imag]) plt.show() def fun(p: float) -> float: h = -2000.0 for a, b in seg: if a.real <= p <= b.real: a += a - b h = max(h, (b.imag - a.imag) * (p - a.real) / (b.real - a.real) + a.imag) for o in road: d = abs(o.real - p) if d < r: h = max(h, o.imag + sqrt(r ** 2 - d ** 2)) return h def cross(a: complex, b: complex, c: complex, d: complex) -> complex: '''Find the intersection of two lines.''' c -= a s1, s2 = ((c + d) * b.conjugate()).imag, (b * c.conjugate()).imag return a + c + d * s2 / (s1 + s2) def simp(l: float, r: float) -> float: '''Calculate the length of an arc that goes through three points.''' mid = (l + r) / 2 a, b, c = map(lambda p: complex(p, fun(p)), [l, mid, r]) v1, v2 = b - a, c - b if abs((v1 * v2.conjugate()).imag) < eps: return abs(v1 + v2) o = cross(a + v1 / 2, v1 * 1j, b + v2 / 2, v2 * 1j) a1, a2 = phase((a - o) * (b - o).conjugate()), phase((b - o) * (c - o).conjugate()) a1, a2 = map(lambda p: p if p >= 0 else p + 2 * pi, [a1, a2]) if a1 + a2 > 2 * pi: a1, a2 = 2 * pi - a1, 2 * pi - a2 return abs(a - o) * (a1 + a2) def inte(l: float, r: float, f: float, step: int) -> float: '''Calculate curve length integral.''' mid = (l + r) / 2 lf, rf = simp(l, mid), simp(mid, r) if step <= 0 and abs(lf + rf - f) < eps: return lf + rf return inte(l, mid, lf, step - 1) + inte(mid, r, rf, step - 1) lp, rp = road[0].real, road[-1].real print(f'{inte(lp, rp, simp(lp, rp), 5):.2f}')
- 1
信息
- ID
- 5925
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 128MiB
- 难度
- 6
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
