1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

szh_AK_all
S挂分挂到被洛谷7级勾卡线|I can do all things搬运于
2025-08-24 22:20:25,当前版本为作者最后更新于2024-10-19 11:56:57,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
在打模拟赛时通过了这题,最终因这题而获得了第一名,写一篇题解纪念下。
分析
可以发现每个墙倒下之后,它所连接的两个数字间的最短路径变为了 ,可能对最终答案产生影响。所以很显然的一点是,我们可以记录一下所有的关键点,最后跑一遍最短路即可。
由于最短路不应该完全是由特殊路径(即倒下的墙)组成的,也就是说,对于两个关键点,我们还需要记录一条普通的边,假设这两个关键点是 ,那么这条边的权值便是 。由于 的范围很大,所以关键点应该离散化一下。
重点在于如何求关键点,也就是对于题目里给出的每个 ,我们需要求出其对应的 。
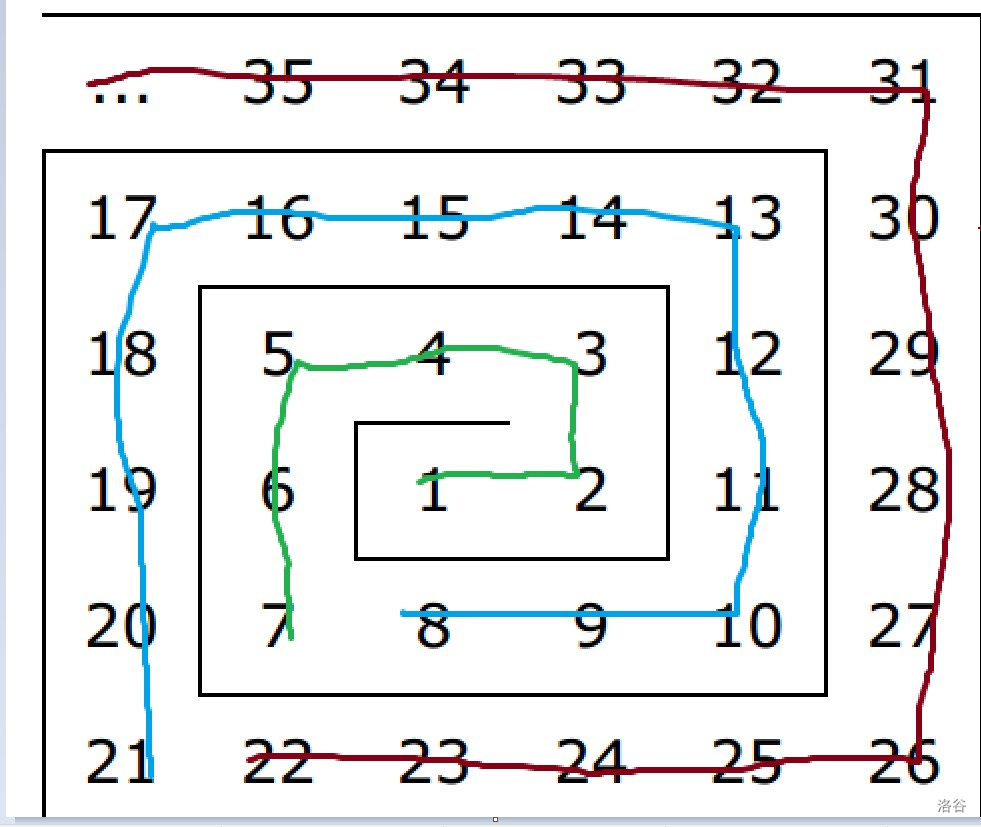
如上图所示,先将迷宫上的点一层层分类,绿色的点代表第一层,蓝色的点代表第二层,依此类推。那么对于一堵墙,它所关联的两个点应是在相邻的层里(除了 连接 的这堵墙)。那么对于每一层,我们还应当将它分为上下左右四个块,从而按照块计算出对应点。
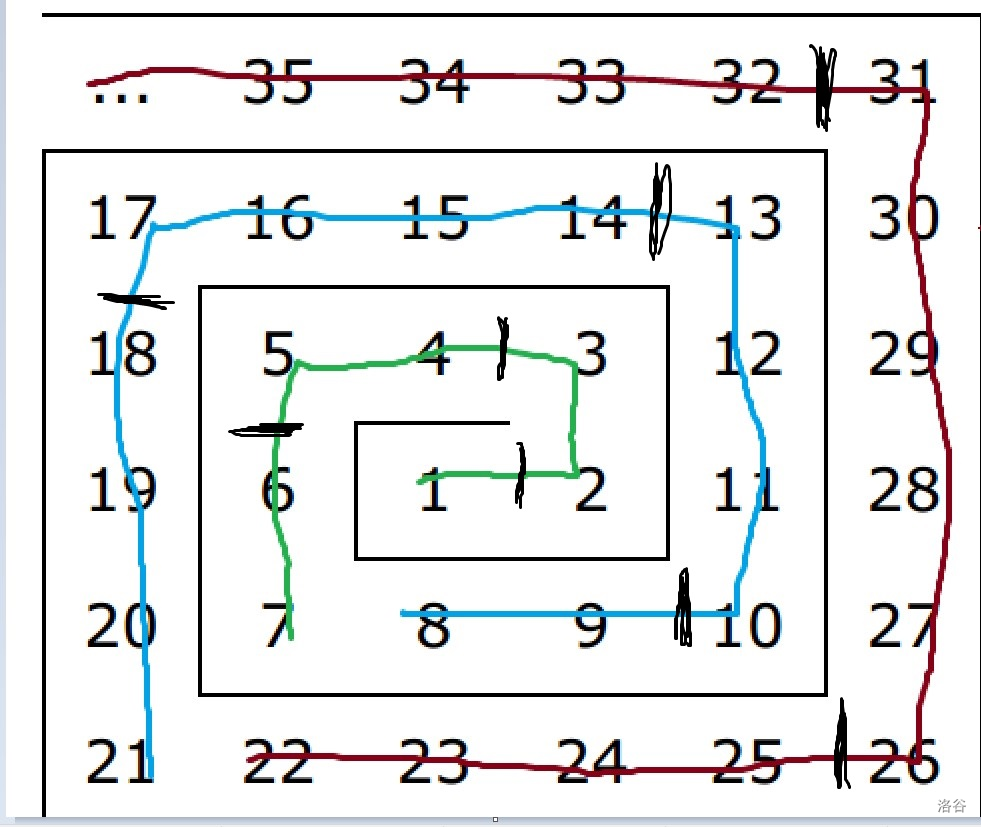
如图,用黑色的线将每一层割成四块,那么除开特殊的第一层,每一层下、右、上、左的块所包含的数量分别为 ,用这样的方法计算,我们可以找出每一层每一块的最小数字(可视为“起点”),从而也可以算出每一层的最小数字和最大数字(即“起点”和“终点”)。
那么在算出当前点对对应的层及块后,它的对应点所在的层便应该是该层的上一层,所在的块应该是该块或者与该块相邻的分界点(因为两层对应块的大小不一样),从而算出对应点的数字号码。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define int long long int a[200005], tot, b[200005]; int xia(int x) { if (x == 1) return 1; if (x == 2) return 8; int la = 21 + 14 * (x - 3) + (x - 3) * (x - 2) / 2 * 8 + 1; return la; } int you(int x) { if (x == 1) return 2; if (x == 2) return 10; int la = 21 + 14 * (x - 3) + (x - 3) * (x - 2) / 2 * 8 + 1; return la + (x - 1) * 2; } int shang(int x) { if (x == 1) return 4; if (x == 2) return 14; int la = 21 + 14 * (x - 3) + (x - 3) * (x - 2) / 2 * 8 + 1; return la + (x - 1) * 2 + x * 2; } int zuo(int x) { if (x == 1) return 6; if (x == 2) return 18; int la = 21 + 14 * (x - 3) + (x - 3) * (x - 2) / 2 * 8 + 1; return la + (x - 1) * 2 + x * 2 + x * 2; } int get(int A) { int l = 1, r = 1000000000, ans = 0; while (l <= r) {//二分计算所在层 int mid = (l + r) / 2; int la, now; if (mid == 1) la = 1, now = 7; else if (mid == 2) la = 8, now = 21; else la = 21 + 14 * (mid - 3) + (mid - 3) * (mid - 2) / 2 * 8 + 1, now = 21 + 14 * (mid - 2) + (mid - 2) * (mid - 1) / 2 * 8; if (la <= A && A <= now) { ans = mid; break; } if (la > A) r = mid - 1; else l = mid + 1; } if (ans == 1)//第一层第二层要特判 return 1; if (ans == 2) { if (A >= 8 && A <= 9) return A - 7; if (A >= 11 && A <= 12) return A - 9; if (A >= 14 && A <= 16) return A - 11; return A - 13; } if (A < you(ans))//块 return A - xia(ans) - 1 + xia(ans - 1); if (A < shang(ans)) return A - you(ans) - 1 + you(ans - 1); if (A < zuo(ans)) return A - shang(ans) - 1 + shang(ans - 1); return A - zuo(ans) - 1 + zuo(ans - 1); } vector<int>g[200005], w[200005]; struct node { int x, dis; friend bool operator<(node l, node r) { return l.dis > r.dis; } node(int aa = 0, int bb = 0) { x = aa; dis = bb; } }; int vis[200005], dis[200005]; void dij() { for (int i = 2; i <= tot; i++) dis[i] = 10000000000000000; priority_queue<node>q; q.push(node(1, 0)); while (!q.empty()) { int x = q.top().x; q.pop(); if (vis[x]) continue; vis[x] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < (int)g[x].size(); i++) { int y = g[x][i], ww = w[x][i]; if (dis[x] + ww < dis[y]) { dis[y] = dis[x] + ww; q.push(node(y, dis[y])); } } } } signed main() { //reopen("maze.in", "r", stdin); //freopen("maze.out", "w", stdout); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; a[++tot] = 1, a[++tot] = n; b[1] = 1, b[2] = n; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { cin >> a[++tot]; b[tot] = a[tot]; a[tot + 1] = get(a[tot]); tot++; b[tot] = a[tot]; //cout << a[tot - 1] << " " << a[tot] << endl; } sort(b + 1, b + tot + 1);//离散化 int nn = unique(b + 1, b + tot + 1) - (b + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) a[i] = lower_bound(b + 1, b + nn + 1, a[i]) - b; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {//特殊边 g[a[i * 2 + 2]].push_back(a[i * 2 + 1]); w[a[i * 2 + 2]].push_back(1); g[a[i * 2 + 1]].push_back(a[i * 2 + 2]); w[a[i * 2 + 1]].push_back(1); } for (int i = 1; i < nn; i++) {//普通边 g[i].push_back(i + 1); w[i].push_back(b[i + 1] - b[i]); g[i + 1].push_back(i); w[i + 1].push_back(b[i + 1] - b[i]); } dij(); for (int i = 1; i <= nn; i++) { if (b[i] == n) { cout << dis[i]; return 0; } } }题解来之不易,看到最后记得点赞喵。
- 1
信息
- ID
- 5441
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 63MiB
- 难度
- 5
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
