1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

Tweetuzki
AFO搬运于
2025-08-24 22:20:03,当前版本为作者最后更新于2020-04-12 14:46:03,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
upt 2020.4.15:加上了部分感性证明和 Bowyer-Watson 算法部分。
upt 2020.4.16:添加了关于判断一个点是否在三角形外接圆内的三维几何方法的证明。
注意:以下内容均在原图无重点、无三点共线、无四点共圆的前提下进行讨论。若原图有这些情况,可以进行一定扰动来避开。
这个算法我是死记下来的,有些地方没有证明,有些地方证明也比较口胡。望请见谅。
本题解仅做概括性归纳整理,想要详细学习该算法可以前往 OI-Wiki 的计算几何 三角剖分页面。
求欧式最小生成树 (EMST) 是 Delaunay 三角剖分最经典的几个应用之一。
一些定义:
-
三角剖分:对于一种平面分割,若对于任意一条未添加的边,都与至少一条已添加的边相交,就称为三角剖分。
-
Delaunay 边:一条边 被称为 Delaunay 边,当且仅当存在一个经过 两点的圆,满足对于任意其它的点 , 都在圆外(这个圆不一定需要是以 为直径的圆)。
-
Delaunay 三角剖分:对于一种三角剖分,如果它保留下的每一条边都是 Delaunay 边,就被称为 Delaunay 三角剖分。
Delaunay 三角剖分主要有以下性质:
- 空圆性:对于剖分出的每一个三角形,其外接圆内均不包含其它点。
- 最小角最大性:Delaunay 三角剖分所剖出的最小角,是所有可能的三角剖分形成的最小角中,最大的。
- 唯一性:Delaunay 三角剖分是唯一的(当然是在没有重点、共线、共圆的前提下)。
空圆性可以用数学归纳法进行证明。
当 时,显然符合条件。
当 时,考虑新插入的那一个点所有相邻三角形的对边。由于其仍然是一条 Delaunay 边,因此必然需要存在一个空圆。那么这条对边所相邻的另一个三角形的外接圆一定不能包含这个新的点,因为一旦包含就会导致以这条边为弦的这个圆无论向哪一端扩张,都始终会含有两个点中的一个,这与 Delaunay 边的定义冲突。如此对新加入的这个点的所有相邻三角形都是满足空圆的,故可数学归纳得到整张 Delaunay 三角剖分是满足空圆性的。
最小角最大性可以这样从空圆性推得:(感谢 @福州周圣力)
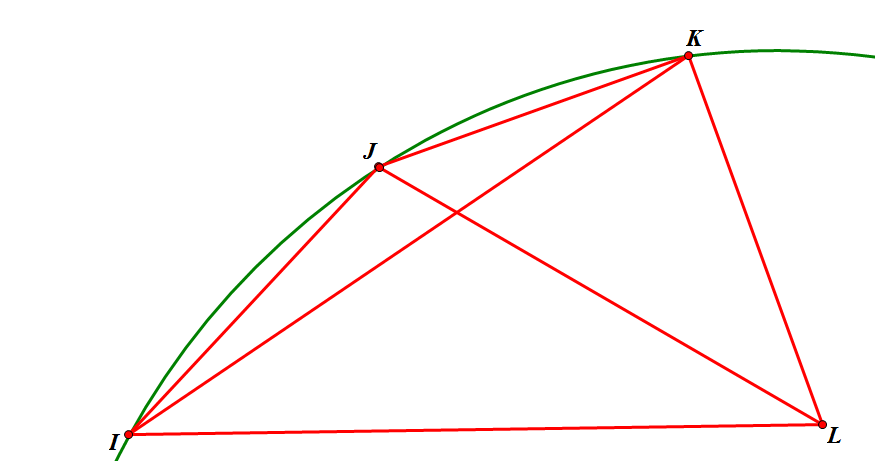
根据 Thales' Theorem,由于 ,所以 在 的外接圆内。
Thales' Theorem:
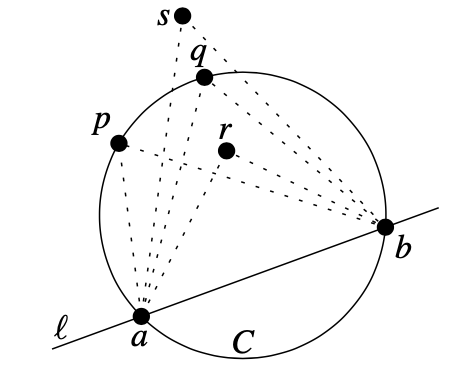
是圆 上与直线 的交点, 在直线 同侧,其中 在圆上, 在圆内, 在圆外,则有如下不等式成立:$\angle arb \gt \angle apb = \angle aqb \gt \angle asb$。
也就是说,如果存在一个点在一个已知三角形的外接圆内,那么这就不满足 Delaunay 三角剖分的空圆性,于是我们就要换一种剖分方式,在换的过程中,必然会使某一个角变大(当然,也会使其它的一部分角变小,如果出现了不合法的变化,即最小角变得更小,那么我们一定可以选择另外一条基准边进行修改)。
唯一性是因为没有四点共圆,从而最小的角度序列是唯一的,它不可能通过调整得到另一个角度序列与它相同的三角剖分。
此外,Delaunay 三角剖分是 Voronoi 图(泰森多边形)的对偶图。对偶图即为,对于一张平面图,将其每块区域抽象为对偶图上的一个点,对偶图中两个点之间有连边当且仅当其对应区域有公共边。
解决此题需要用到的结论:欧式最小生成树的边集是 Delaunay 三角剖分边集的子集。
一种理解方法根据 Voronoi 图。由于 Delaunay 三角剖分是 Voronoi 图的对偶图,那么我们想象,Voronoi 图是由每一个点同时向外扩张得到的。
若现在扩张半径为 ,则原图上所有欧氏距离不超过 的点都被连上了。这类似于一个 Kruskal 的过程,当两块连通块第一次碰撞的时候,也就是欧式最小生成树上两块连通块第一次连通的时候。
可以结合下图进行理解。图片来源

还有一种证明,使用反证法,设最小生成树中那条不在 Delaunay 三角剖分中的边为 。由于其不在 Delaunay 三角剖分中,因此以它为直径的圆内或圆上,会存在一个其它点 。
我们将 这条边割开,连接 或 ,显然这样图还是联通的。但由于 是直径,长度大于 和 。如此,我们找到了一棵更优的生成树,所以 这样的边不会存在于最小生成树中。
实现 Delaunay 三角剖分的若干方法中,一种比较常用的方法是增量构造的 Bowyer-Watson 算法,朴素实现复杂度是 。
Bowyer-Watson 算法基于 Delaunay 三角剖分的局部最优性,假设我们已经构造好了前 个点的 Delaunay 三角剖分,现在插入第 个点。由于 Delaunay 三角剖分需要满足空圆特性,这张剖出的三角网上,所有内含第 个点的三角形都是不合法的,我们将其扔掉,形成一个内部的凸多边形形状的空腔,我们称之为 Delaunay 空腔。得到 Delaunay 空腔后,将空腔上的点与第 个点相连,就构造成了前 个点的 Delaunay 三角剖分。
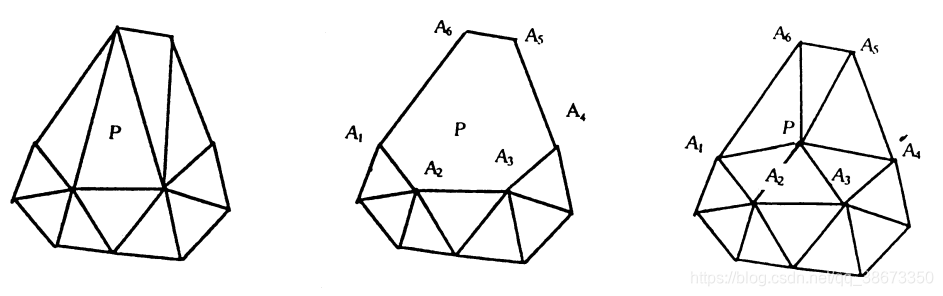
关于 Delaunay 空腔的查找与维护,可以使用 Jonathan Shewchuk 教授提出的三角形链表结构。
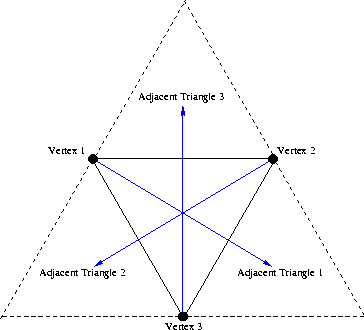
对三角形的每个点,其邻接指针指向它对边所相邻的三角形。特殊地,若对边是凸包上的边,外侧是一个无限的平面的话,该指针指向 NULL。
这样,我们可以先找到新加入的第 个点在哪一个三角形内,然后从这个三角形开始不断检验相邻的三角形是否合法,就能扩张出一个 Delaunay 空腔。
另一种比较常用的方法是 Guibas、Stolfi 的分治算法,复杂度 。
算法大致如下(此部分引用图片均来源于上述文章)。
我们将这些点水平序排序,分治进行处理。当点数不超过 时,直接构造返回。
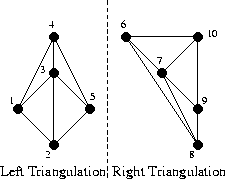
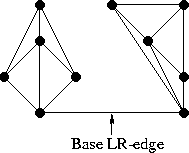
考虑合并,我们首先找到一条 Base LR-edge,它是连接两部分的、最底下的、且与构造好的边都不相交的那条边。
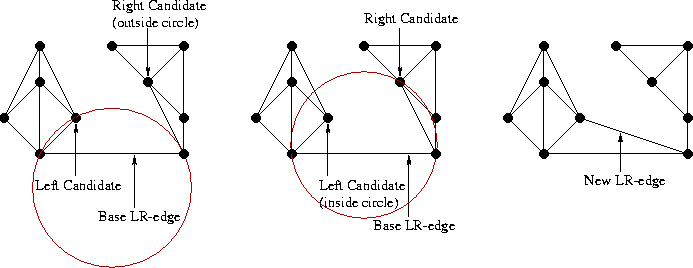
再枚举这条边所连的两端点上,与端点相邻的,与该边夹角小于 的所有点。由于 Delaunay 三角剖分具有唯一性,这么多点中只有一个点,满足与 Base LR-edge 两端点组成的三角形不包含其它点。“打擂台” 方式找出这个点即可。
然后插入这个点与 Base LR-edge 端点之间的边,删去与该边相交的已构造好的边。再将该边作为 Base LR-edge 重复此过程,直到再无法添加新边为止。
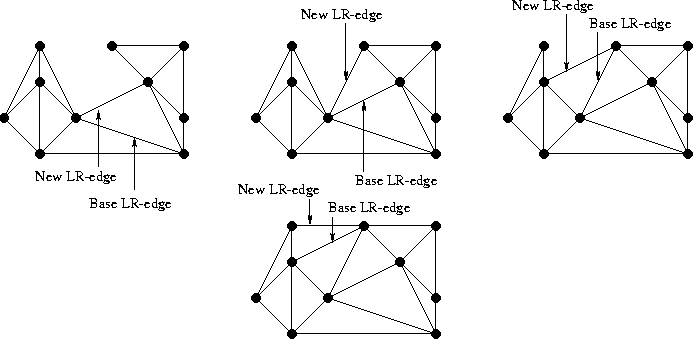
每条边均摊只会被访问一次,因此我们做到了线性的合并。这个分治算法的复杂度是 。
另外,对于精度要格外注意。
本题中,我们需要判断一个点 是否在三个点 的外接圆内。一般的想法是:
- 求出 的中垂线,求交得到圆心,在算出半径,然后比较圆心到 的距离和半径来确定 是否在圆内。
- 根据叉积判断 是否在 同侧。若在同侧,则 在圆内的充要条件为 ,根据同弦所对圆周角相等可以简单证明;若在异侧,则 在圆内的充要条件为 ,根据圆内接四边形对角互补可以简单证明。
以上两种方法精度丢失都非常严重,不宜使用。在本题中,我们用三维几何进行判断。
将每一个平面内的点 映射到空间内的 。则点 在 的外接圆内的充要条件为,点 在 三点所构成平面之下。
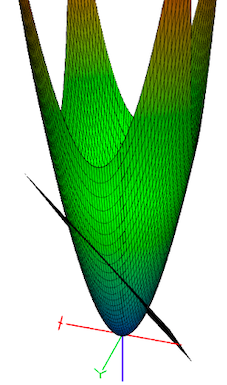
此部分参考了周雨扬的《IOI2020中国国家集训队作业解题报告》Sasha Circle 部分。
这是因为,我们不妨设该平面方程为 。则 三点都落在该平面与抛物面 相交的位置上。对于抛物面上的所有点,所有在被截图形内部的点都落在了平面之下,其余点都落在了平面之上。那么我们现在只需证明,平面 截抛物面 在平面 的投影上为一个圆。
列方程得 ,配方得 $\displaystyle \left(x+ \frac{a}{2} \right)^2+\left(y+\frac{b}{2}\right)^2=c+\frac{a^2+b^2}{4}$。这即为圆的方程。
这就证明了,平面 上所有在圆内部的点,映射到抛物面上会落在被截区域中间,位于平面 之下;所有不在圆内部的点,就位于平面 之上。
判断点与平面关系,可以先三维叉积算出平面的法线,再用三维点积判断与法线夹角为锐角还是钝角,从而可以确定该点在平面之上还是平面之下。
这种方法精度较高,可以很好地减小误差。
对于本题,分治求一下 Delaunay 三角剖分,然后再跑一个最小生成树算法即可。
可为什么边数是正确的呢?我们设总点数为 ,凸包上的点有 个,三角形个数为 ,则面数 。对于每一个三角形,它有三条边相邻,凸包上有 条边,且每条边只与两个面相交(抑或是三角形与三角形,抑或是三角形与外侧的无穷平面),故而得出边数的表达式 。代入欧拉公式 ,解得 ,从而推出 。
对于一般情况,凸包上的点数至少为 ,故而边数不会超过 。进而将稠密图问题转化为稀疏图问题,时间复杂度优化至 。
代码:
Bowyer-Watson(50 分):
#include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <utility> #include <vector> const int MaxN = 5005; const int MaxF = 200000; const double eps = 1e-9; #ifdef Tweetuzki #define debug(arg...) fprintf(stderr, arg) #else #define debug(arg...) void(0) #endif typedef struct vec_t { double x, y; vec_t(double _x = 0, double _y = 0) { x = _x, y = _y; } inline friend vec_t operator+(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return vec_t(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y); } inline friend vec_t operator-(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return vec_t(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y); } inline friend vec_t operator*(const vec_t &a, double k) { return vec_t(a.x * k, a.y * k); } inline friend double dot(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y; } inline friend double cross(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x; } inline friend double mod(const vec_t &a) { return sqrt(a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y); } inline void shake() { if (rand() % 2 == 0) x += 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; else x -= 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; if (rand() % 2 == 0) y += 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; else y -= 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; } } node_t; typedef struct vec3_t { double x, y, z; vec3_t(double _x = 0, double _y = 0, double _z = 0) { x = _x, y = _y, z = _z; } inline friend vec3_t operator+(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y, a.z + b.z); } inline friend vec3_t operator-(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y, a.z - b.z); } inline friend vec3_t operator*(const vec3_t &a, double k) { return vec3_t(a.x * k, a.y * k, a.z * k); } inline friend vec3_t cross(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, a.z * b.x - a.x * b.z, a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x); } inline friend double dot(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z; } } node3_t; struct triangle_t { int a, b, c; int la, lb, lc; triangle_t(int _a = 0, int _b = 0, int _c = 0, int _la = 0, int _lb = 0, int _lc = 0) { a = _a, b = _b, c = _c; la = _la, lb = _lb, lc = _lc; } }; struct edge_t { int u, v; double w; edge_t(int _u = 0, int _v = 0, double _w = 0) { u = _u, v = _v, w = _w; } inline friend bool operator<(const edge_t &a, const edge_t &b) { return a.w < b.w; } }; int N, CntF; node_t A[MaxN + 5]; triangle_t F[MaxF + 5]; bool Del[MaxF + 5]; inline vec3_t mapping(const vec_t &a) { return vec3_t(a.x, a.y, a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y); } inline bool inCircumcircle(const node_t &a, const node_t &b, const node_t &c, const node_t &p) { node3_t _a = mapping(a), _b = mapping(b), _c = mapping(c), _p = mapping(p); if (cross(b - a, c - a) < 0) std::swap(_b, _c); node3_t normal = cross(_b - _a, _c - _a); if (dot(normal, _p - _a) > eps) return false; else return true; } inline bool inCircumcircle(const triangle_t &t, const node_t &p) { return inCircumcircle(A[t.a], A[t.b], A[t.c], p); } void init() { scanf("%d", &N); for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) { scanf("%lf %lf", &A[i].x, &A[i].y); A[i].shake(); } A[N + 1] = node_t(-1e6, -1e6), A[N + 2] = node_t(-1e6, 1e6); A[N + 3] = node_t(1e6, -1e6), A[N + 4] = node_t(1e6, 1e6); F[++CntF] = triangle_t(N + 1, N + 3, N + 2, 2, 0, 0); F[++CntF] = triangle_t(N + 4, N + 2, N + 3, 1, 0, 0); } std::vector< std::pair<int, int> > Lk[MaxN + 5]; int To[MaxN + 5], Tof[MaxN + 5]; int NodeStk[MaxN + 5], NodeTp; void dfs(int u, int f, int beg) { debug("dfs(%d, %d, %d)\n", u, f, beg); if (u == beg) { if (f != 0) return; NodeStk[NodeTp++] = u; auto p = *(Lk[u].begin()); To[u] = p.first; Tof[u] = p.second; dfs(p.first, u, beg); } else { NodeStk[NodeTp++] = u; for (auto p : Lk[u]) { if (p.first == f) continue; To[u] = p.first; Tof[u] = p.second; dfs(p.first, u, beg); } } } inline bool cmp(int a, int b, int c, int d) { if (a == c && b == d) return true; if (a == d && b == c) return true; return false; } inline void insert(int insertNode) { static int stk[MaxF + 5]; int tp = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= CntF; ++i) if (Del[i] == false && inCircumcircle(F[i], A[insertNode]) == true) { stk[++tp] = i; Del[i] = true; } for (int i = 1; i <= tp; ++i) debug("stk[%d] = %d\n", i, stk[i]); static int e[MaxF + 5][3]; int cnte = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= tp; ++i) { int x = stk[i]; if (F[x].la == 0) { cnte++; e[cnte][0] = F[x].b, e[cnte][1] = F[x].c, e[cnte][2] = 0; } else if (inCircumcircle(F[F[x].la], A[insertNode]) == false) { int y = F[x].la; cnte++; if (F[y].la == x) { F[y].la = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].b, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else if (F[y].lb == x) { F[y].lb = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else { F[y].lc = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].b, e[cnte][2] = y; } } if (F[x].lb == 0) { cnte++; e[cnte][0] = F[x].a, e[cnte][1] = F[x].c, e[cnte][2] = 0; } else if (inCircumcircle(F[F[x].lb], A[insertNode]) == false) { int y = F[x].lb; cnte++; if (F[y].la == x) { F[y].la = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].b, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else if (F[y].lb == x) { F[y].lb = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else { F[y].lc = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].b, e[cnte][2] = y; } } if (F[x].lc == 0) { cnte++; e[cnte][0] = F[x].a, e[cnte][1] = F[x].b, e[cnte][2] = 0; } else if (inCircumcircle(F[F[x].lc], A[insertNode]) == false) { int y = F[x].lc; cnte++; if (F[y].la == x) { F[y].la = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].b, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else if (F[y].lb == x) { F[y].lb = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].c, e[cnte][2] = y; } else { F[y].lc = -1; e[cnte][0] = F[y].a, e[cnte][1] = F[y].b, e[cnte][2] = y; } } } for (int i = 1; i <= cnte; ++i) debug("e[%d] = (%d, %d, %d)\n", i, e[i][0], e[i][1], e[i][2]); for (int i = 1; i <= cnte; ++i) { Lk[e[i][0]].emplace_back(e[i][1], e[i][2]); Lk[e[i][1]].emplace_back(e[i][0], e[i][2]); } NodeTp = 0; dfs(e[1][0], 0, e[1][0]); for (int i = 0; i < NodeTp; ++i) debug("node = %d, to = %d, tof = %d\n", NodeStk[i], To[NodeStk[i]], Tof[NodeStk[i]]); for (int i = 0; i < NodeTp; ++i) { int id = CntF + (i % NodeTp) + 1; F[id] = triangle_t(insertNode, NodeStk[i], To[NodeStk[i]], Tof[NodeStk[i]], CntF + ((i + 1) % NodeTp) + 1, CntF + ((i - 1 + NodeTp) % NodeTp) + 1); if (Tof[NodeStk[i]] != 0) { int y = Tof[NodeStk[i]]; if (F[y].la == -1 && cmp(NodeStk[i], To[NodeStk[i]], F[y].b, F[y].c)) F[y].la = id; if (F[y].lb == -1 && cmp(NodeStk[i], To[NodeStk[i]], F[y].a, F[y].c)) F[y].lb = id; if (F[y].lc == -1 && cmp(NodeStk[i], To[NodeStk[i]], F[y].a, F[y].b)) F[y].lc = id; } } CntF += NodeTp; for (int i = 0; i < NodeTp; ++i) Lk[NodeStk[i]].clear(); for (int i = 1; i <= CntF; ++i) debug("i = %d, a = %d, b = %d, c = %d, la = %d, lb = %d, lc = %d, del = %d\n", i, F[i].a, F[i].b, F[i].c, F[i].la, F[i].lb, F[i].lc, Del[i]); } int CntE, Par[MaxN + 5]; edge_t ME[MaxF + 5]; int find(int x) { return x == Par[x] ? x : Par[x] = find(Par[x]); } void solve() { for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) insert(i); for (int i = 1; i <= CntF; ++i) if (Del[i] == false) debug("i = %d, a = %d, b = %d, c = %d, l = (%d, %d, %d)\n", i, F[i].a, F[i].b, F[i].c, F[i].la, F[i].lb, F[i].lc); for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) Par[i] = i; for (int i = 1; i <= CntF; ++i) { if (F[i].a <= N && F[i].b <= N) ME[++CntE] = edge_t(F[i].a, F[i].b, mod(A[F[i].a] - A[F[i].b])); if (F[i].a <= N && F[i].c <= N) ME[++CntE] = edge_t(F[i].a, F[i].c, mod(A[F[i].a] - A[F[i].c])); if (F[i].b <= N && F[i].c <= N) ME[++CntE] = edge_t(F[i].b, F[i].c, mod(A[F[i].b] - A[F[i].c])); } std::sort(ME + 1, ME + 1 + CntE); double ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= CntE; ++i) { int p = find(ME[i].u), q = find(ME[i].v); if (p != q) { Par[p] = q; ans += ME[i].w; } } printf("%lf\n", ans); } int main() { #ifdef Tweetuzki freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin); freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); freopen("errorfile.txt", "w", stderr); #endif init(); solve(); return 0; }Guibas-Stolfi:
#include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <ctime> const int MaxN = 100000, MaxM = 2000000; const double eps = 1e-9; typedef struct vec_t { double x, y; vec_t(double _x = 0, double _y = 0) { x = _x, y = _y; } inline friend vec_t operator+(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return vec_t(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y); } inline friend vec_t operator-(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return vec_t(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y); } inline friend vec_t operator*(const vec_t &a, double k) { return vec_t(a.x * k, a.y * k); } inline friend double dot(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y; } inline friend double cross(const vec_t &a, const vec_t &b) { return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x; } inline friend double mod(const vec_t &a) { return sqrt(a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y); } inline void shake() { if (rand() % 2 == 0) x += 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; else x -= 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; if (rand() % 2 == 0) y += 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; else y -= 1.0 * rand() / RAND_MAX * eps; } } node_t; typedef struct vec3_t { double x, y, z; vec3_t(double _x = 0, double _y = 0, double _z = 0) { x = _x, y = _y, z = _z; } inline friend vec3_t operator+(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y, a.z + b.z); } inline friend vec3_t operator-(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y, a.z - b.z); } inline friend vec3_t cross(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return vec3_t(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, a.z * b.x - a.x * b.z, a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x); } inline friend double dot(const vec3_t &a, const vec3_t &b) { return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z; } } node3_t; struct Graph { int cnte; int head[MaxN + 5], to[MaxM * 2 + 5]; int pre[MaxM * 2 + 5], nxt[MaxM * 2 + 5]; Graph() { cnte = 1; memset(head, 0, sizeof head); memset(to, 0, sizeof to); memset(pre, 0, sizeof pre); memset(nxt, 0, sizeof nxt); } inline void addEdge(int u, int v) { cnte++; to[cnte] = v; nxt[cnte] = head[u]; pre[head[u]] = cnte; head[u] = cnte; } inline void delEdge(int id) { if (pre[id] != 0) nxt[pre[id]] = nxt[id]; if (nxt[id] != 0) pre[nxt[id]] = pre[id]; if (head[to[id ^ 1]] == id) head[to[id ^ 1]] = nxt[id]; } }; struct Tree { int cnte; int head[MaxN + 5], nxt[MaxN * 2 + 5], to[MaxN * 2 + 5]; double val[MaxN * 2 + 5]; inline void addEdge(int u, int v, double w) { cnte++; to[cnte] = v; val[cnte] = w; nxt[cnte] = head[u]; head[u] = cnte; } }; struct edge_t { int u, v; double w; edge_t(int _u = 0, int _v = 0, double _w = 0) { u = _u, v = _v, w = _w; } inline friend bool operator<(const edge_t &a, const edge_t &b) { return a.w < b.w; } }; int N, M, Q; node_t A[MaxN + 5], MemoryA[MaxN + 5]; int Indice[MaxN + 5]; int Par[MaxN + 5]; edge_t E[MaxM + 5]; Graph Gr; clock_t st = clock(); template <typename Int> inline Int max(Int a, Int b) { return a > b ? a : b; } inline node3_t mapping(const node_t &a) { return vec3_t(a.x, a.y, a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y); } inline bool inCircumcircle(const node_t &a, const node_t &b, const node_t &c, const node_t &p) { node3_t _a = mapping(a), _b = mapping(b), _c = mapping(c), _p = mapping(p); if (cross(b - a, c - a) < 0) std::swap(_b, _c); node3_t normal = cross(_b - _a, _c - _a); if (dot(normal, _p - _a) > eps) return false; else return true; } inline bool intersect(const node_t &a, const node_t &b, const node_t &c, const node_t &d) { if (cross(c - a, b - a) * cross(b - a, d - a) < eps) return false; if (cross(a - d, c - d) * cross(c - d, b - d) < eps) return false; return true; } void init() { srand(20040313U); scanf("%d", &N); for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) { double x, y; scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y); A[i].x = x, A[i].y = y; MemoryA[i] = A[i]; A[i].shake(); } } inline bool levelCompare(int x, int y) { return A[x].x < A[y].x; } inline std::pair<int, int> getInitialBaseEdge(int l, int r) { int m = (l + r) >> 1; static int stk[MaxN + 5]; int tp = 0; stk[++tp] = l, stk[++tp] = l + 1; for (int i = l + 2; i <= r; ++i) { while (tp > 1 && cross(A[Indice[stk[tp]]] - A[Indice[stk[tp - 1]]], A[Indice[i]] - A[Indice[stk[tp]]]) < eps) tp--; stk[++tp] = i; } for (int i = 1; i < tp; ++i) if (stk[i] <= m && stk[i + 1] > m) return std::make_pair(Indice[stk[i]], Indice[stk[i + 1]]); return std::make_pair(-1, -1); } void fun(int l, int r) { if (l == r) return; if (l + 1 == r) { Gr.addEdge(Indice[l], Indice[r]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[r], Indice[l]); return; } if (l + 2 == r) { Gr.addEdge(Indice[l], Indice[l + 1]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[l + 1], Indice[l]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[l], Indice[l + 2]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[l + 2], Indice[l]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[l + 1], Indice[l + 2]); Gr.addEdge(Indice[l + 2], Indice[l + 1]); return; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; fun(l, m), fun(m + 1, r); std::pair<int, int> base = getInitialBaseEdge(l, r); for (;;) { Gr.addEdge(base.first, base.second); Gr.addEdge(base.second, base.first); int leftFinal = -1, rightFinal = -1; for (int i = Gr.head[base.first]; i; i = Gr.nxt[i]) { int candidate = Gr.to[i]; if (cross(A[base.second] - A[base.first], A[candidate] - A[base.first]) < eps) continue; if (leftFinal == -1 || inCircumcircle(A[base.first], A[base.second], A[leftFinal], A[candidate]) == true) leftFinal = candidate; } for (int i = Gr.head[base.second]; i; i = Gr.nxt[i]) { int candidate = Gr.to[i]; if (cross(A[candidate] - A[base.second], A[base.first] - A[base.second]) < eps) continue; if (rightFinal == -1 || inCircumcircle(A[base.first], A[base.second], A[rightFinal], A[candidate]) == true) rightFinal = candidate; } if (leftFinal == -1 && rightFinal == -1) break; if (leftFinal != -1 && rightFinal != -1) { if (inCircumcircle(A[base.first], A[base.second], A[leftFinal], A[rightFinal]) == true) leftFinal = -1; else rightFinal = -1; } if (leftFinal != -1) { for (int i = Gr.head[base.first]; i; i = Gr.nxt[i]) { int linknode = Gr.to[i]; if (intersect(base.second, leftFinal, base.first, linknode) == true) { Gr.delEdge(i); Gr.delEdge(i ^ 1); } } base = std::make_pair(leftFinal, base.second); } else { for (int i = Gr.head[base.second]; i; i = Gr.nxt[i]) { int linknode = Gr.to[i]; if (intersect(base.first, rightFinal, base.second, linknode) == true) { Gr.delEdge(i); Gr.delEdge(i ^ 1); } } base = std::make_pair(base.first, rightFinal); } } } int find(int x) { return x == Par[x] ? x : Par[x] = find(Par[x]); } void solve() { for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) Indice[i] = i; std::sort(Indice + 1, Indice + 1 + N, levelCompare); fun(1, N); fprintf(stderr, "Delaunay = %lf s\n", 1.0 * (clock() - st) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); for (int u = 1; u <= N; ++u) for (int i = Gr.head[u]; i; i = Gr.nxt[i]) { int v = Gr.to[i]; if (u < v) E[++M] = edge_t(u, v, mod(MemoryA[v] - MemoryA[u])); } double ans = 0; std::sort(E + 1, E + 1 + M); for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) Par[i] = i; for (int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) { int u = E[i].u, v = E[i].v; double w = E[i].w; int p = find(u), q = find(v); if (p != q) { ans += w; Par[p] = q; } } printf("%lf\n", ans); } int main() { init(); solve(); return 0; } -
- 1
信息
- ID
- 5378
- 时间
- 1500ms
- 内存
- 256MiB
- 难度
- 7
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
