1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

Azuree
What really matters is always very simple.搬运于
2025-08-24 22:14:37,当前版本为作者最后更新于2020-08-03 18:52:10,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
根据题意,我们可以把位于同一行且左右相邻的点连成一条横边,把位于同一列且上下相邻的点连成一条竖边(这里的“相邻”指的是两个点在横向或竖向上之间没有输入给出的黑点,一个点可以参与多条边)。
比如,我们可以把一个图连成这样:
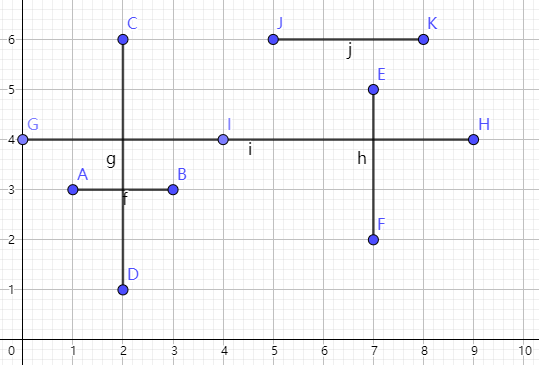
那么,不难发现,能够变成黑点的白点都是位于线段交点上的点。
那么,如何去统计线段交点呢?
我们可以把可以把边分成两类:横向边(和x轴平行的边)和纵向边(和y轴平行的边)。于是,统计交点就等同于每条横向边于纵向 边交点个数的和。而对于这个和,我们可以用扫描线的方法求得。
大体思路是这样的:
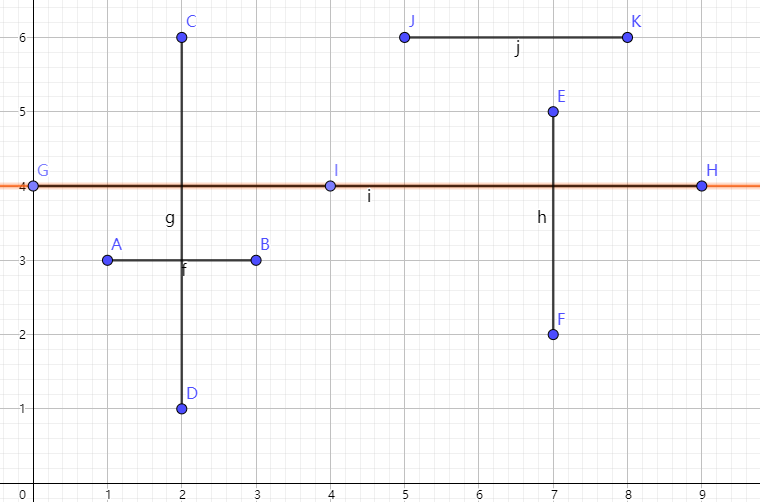
如果扫描线是从上到下进行扫描的,则我们可以用
线段树树状数组来记录有多少条纵向边经过了。为了方便理解,我们可以先用一个最普通的数组来记录纵边经过点的距离。如下图,若我们以为例,则,其中两个表示的便是两个交点。而对于查询,交点数量便是线段GI、线段IH上交点数量的和。我们发现,如果直接在刚刚的数组中统计,那么复杂度为。我们可以用树状数组来优化这一步,来完成这个本质上是区间求和的工作。
对于树状数组的修改,我们只需在纵边的第一个点被扫到时在数组的对应位置加一,在纵边的第二个点被扫到后在对应位置减一即可。
code:
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #define ll long long #define INF 0x7fffffff #define qwq printf("qwq\n"); using namespace std; int read() { register int x = 0,f = 1;register char ch; ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0'){if(ch == '-') f = -f;ch = getchar();} while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0'){x = x * 10 + ch - 48;ch = getchar();} return x * f; } struct node { int x, y; }u[400005]; struct edge { int up, down, left, right; }e[400005]; struct edge_end { int x, y; bool operator < (const edge_end &a) const {return a.y < y;} }; int n, m, cnt, ans, maxx, a[400005], t[400005]; priority_queue<edge_end> que; void Read_in() { n = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { u[i].x = read(); u[i].y = read(); a[++cnt] = u[i].x; a[++cnt] = u[i].y; } } void Discretization() { sort(a + 1, a + cnt + 1); cnt = unique(a + 1, a + cnt + 1) - a - 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { u[i].x = lower_bound(a + 1, a + cnt + 1, u[i].x) - a; u[i].y = lower_bound(a + 1, a + cnt + 1, u[i].y) - a; maxx = max(maxx, u[i].x); } } bool xsort(node a, node b) {return a.x == b.x ? a.y < b.y : a.x < b.x;} bool ysort(node a, node b) {return a.y == b.y ? a.x < b.x : a.y < b.y;} bool esort(edge a, edge b) {return a.up == b.up ? a.left < b.left : a.up < b.up;} void Make_edge() { sort(u + 1, u + n + 1, xsort); // x 相同 处理竖边 for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if(u[i + 1].x != u[i].x || u[i + 1].y - u[i].y < 2) continue; e[++m].up = u[i].y + 1; e[m].down = u[i + 1].y - 1; e[m].right = u[i].x; } sort(u + 1, u + n + 1, ysort); // y 相同 处理横边 for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if(u[i + 1].y != u[i].y || u[i + 1].x - u[i].x < 2) continue; e[++m].up = u[i].y; e[m].left = u[i].x + 1; e[m].right = u[i + 1].x - 1; } sort(e + 1, e + m + 1, esort); } int lowbit(int x) {return x & -x;} void update(int x, int k) {while(x <= maxx) {t[x] = t[x] + k; x = x + lowbit(x);}} int query(int x) {int ans = 0; while(x) {ans = ans + t[x]; x = x - lowbit(x);} return ans;} void Scanning() { for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int deep = e[i].up; while(!que.empty() && que.top().y <= deep) {update(que.top().x, -1); que.pop();} if(!e[i].left) {update(e[i].right, 1); que.push((edge_end){e[i].right, e[i].down + 1});} else {ans = ans + query(e[i].right) - query(e[i].left - 1);} } } void Print() {printf("%d\n", ans + n);} int main() { Read_in(); Discretization(); Make_edge(); Scanning(); Print(); return 0; }
- 1
信息
- ID
- 4823
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 125MiB
- 难度
- 6
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
