1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

xgzc
苔花如米小,也学牡丹开。搬运于
2025-08-24 22:11:49,当前版本为作者最后更新于2019-08-30 20:24:53,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
将和分别看成和,并将它投射到平面直角坐标系上,那么我们就是想找到最小的点。
先找出最小的点以及最小的点,接下来我们就需要求出一个点,使得在左侧且距离最远。
也就是让最大,即$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AC}}$最小(因为$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AC}} < 0$)
$$\begin{aligned}\because \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AC}} &= (x_{\mathrm{B}} - x_{\mathrm{A}})(y_{\mathrm{C}} - y_{\mathrm{A}}) - (y_{\mathrm{B}} - y_{\mathrm{A}})(x_\mathrm{C} - x_\mathrm{A}) \\&= (x_\mathrm B - x_\mathrm A) \times y_\mathrm C + (y_\mathrm A - y_\mathrm B) \times x_\mathrm C + y_\mathrm B x_\mathrm A - x_\mathrm B y_\mathrm A\end{aligned} $$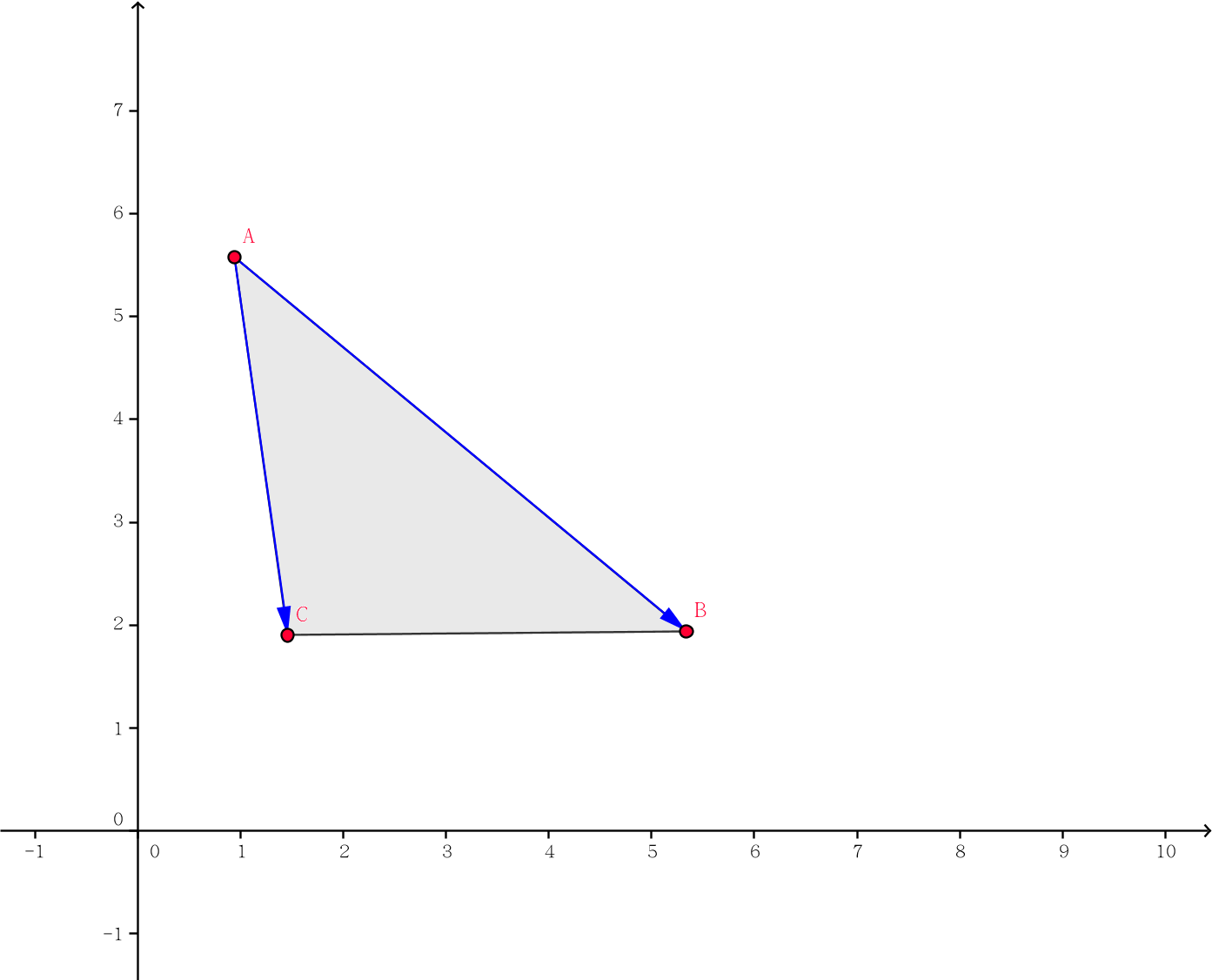
所以考虑最小化$(x_\mathrm B - x_\mathrm A) \times y_\mathrm C + (y_\mathrm A - y_\mathrm B) \times x_\mathrm C$。
于是可以直接将边权改为$w_i = (y_\mathrm A - y_\mathrm B) \times a_i + (x_\mathrm B - x_\mathrm A)\times b_i$,跑最小生成树算法即可得到点。
接下来递归处理即可。
这个过程中我们可以知道,决策点构成了一个含有个点的凸包。因为在个点的凸包上的点数期望是的,所以复杂度为。
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> inline int read() { int data = 0, w = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (ch != '-' && (ch < '0' || ch > '9')) ch = getchar(); if (ch == '-') w = -1, ch = getchar(); while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') data = data * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar(); return data * w; } const int N(205), M(10010); struct vector { int x, y; }; vector ans = (vector) {(int) 1e9, (int) 1e9}; inline vector operator - (const vector &lhs, const vector &rhs) { return (vector) {lhs.x - rhs.x, lhs.y - rhs.y}; } inline int operator * (const vector &lhs, const vector &rhs) { return lhs.x * rhs.y - lhs.y * rhs.x; } void chkmin(vector &x, vector y) { long long _x = 1ll * x.x * x.y, _y = 1ll * y.x * y.y; if (_x > _y || (_x == _y && x.x > y.x)) x = y; } int n, m, fa[N], rnk[N]; int find(int x) { return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); } int merge(int x, int y) { x = find(x), y = find(y); return (rnk[x] == rnk[y] ? fa[x] = y, ++rnk[y] : (rnk[x] < rnk[y] ? fa[x] = y : fa[y] = x)); } struct edge { int x, y, a, b, w; } e[M]; inline int operator < (const edge &lhs, const edge &rhs) { return lhs.w < rhs.w; } vector Kruskal() { vector res = (vector) {0, 0}; int cnt = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i, rnk[i] = 1; std::sort(e + 1, e + m + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= m && cnt < n - 1; i++) { int x = find(e[i].x), y = find(e[i].y); if (x != y) merge(x, y), res.x += e[i].a, res.y += e[i].b, ++cnt; } return res; } void solve(const vector &A, const vector &B) { for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) e[i].w = e[i].a * (A.y - B.y) + e[i].b * (B.x - A.x); vector C = Kruskal(); chkmin(ans, C); if ((B - A) * (C - A) >= 0) return; solve(A, C), solve(C, B); } int main() { n = read(), m = read(); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) e[i] = (edge) {read() + 1, read() + 1, read(), read(), 0}; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) e[i].w = e[i].a; vector A = Kruskal(); chkmin(ans, A); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) e[i].w = e[i].b; vector B = Kruskal(); chkmin(ans, B); solve(A, B); printf("%d %d\n", ans.x, ans.y); return 0; }
- 1
信息
- ID
- 4532
- 时间
- 2000ms
- 内存
- 64MiB
- 难度
- 7
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
