1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

crashed
让我们登上这座山!搬运于
2025-08-24 22:10:39,当前版本为作者最后更新于2019-08-15 21:19:49,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
题目
点这里看题目。
分析
计算几何第一题,然后
不负众望地爆炸了。
考场上一个很简单的优化居然都没有想到......太菜了。
这道题其实是扫描线+维护。
首先,我们来一个预备知识点——线段判交。
看博客吧。
有了这个知识之后我们就可以开始题解了。
我们的主要思路就是先找出任意两条相交的线段,此时答案就在两条之间,接下来再搞就容易了。
于是我们的目标就是优化第一步。
先对所有的点排序,按照优先次后的顺序。然后扫描点的序列。
在这之前,我们得了解这个到底存的什么。简单来说,当当前位置为时,维护的就是在x轴的投影上包含了这个点的不相交线段的集合。
所以根据这个原则,我们可以按如下方法维护:
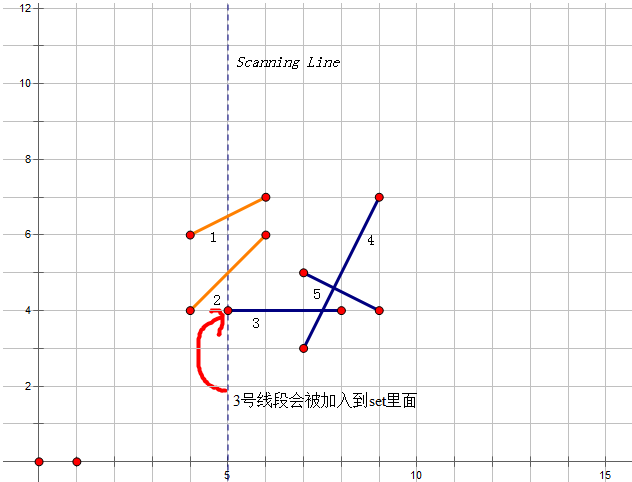
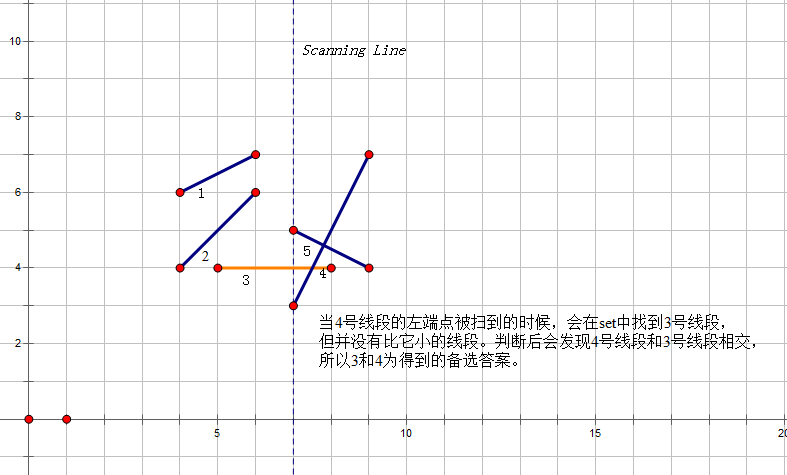
1.如果当前的点是一个线段的起点,我们就可以在中找出当前线段相对的前后线段。如果找出的前后线段中的一个和当前线段有交点,就取出相交的一对检查答案;否则就插入当前线段。
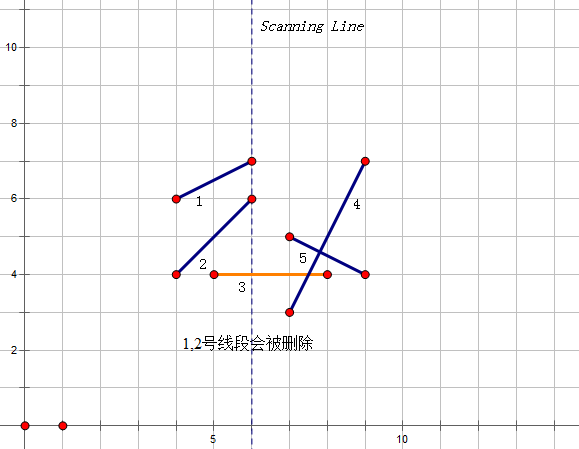
2.如果当前的点是一个线段的终点,我们先在中找出当前线段的前驱后继。如果找到的两个线段有交点,就取出来检查答案;否则就删除当前线段。
其实所有线段检查的操作都是为了避免在更新后集合中出现相交的线段,把握这一点的话就不难写了。
另外,由于中的线段不相交,所以说两个在中的线段的上下关系不会变,我们可以利用这一点来对线段进行排序。
图例:
插入一个线段:
删除一个线段:
找出相交:
以及喜闻乐见的代码。代码
#include <set> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int MAXN = 1e5 + 5; template<typename _T> void read( _T &x ) { x = 0;char s = getchar();int f = 1; while( s > '9' || s < '0' ){if( s == '-' ) f = -1; s = getchar();} while( s >= '0' && s <= '9' ){x = ( x << 3 ) + ( x << 1 ) + ( s - '0' ), s = getchar();} x *= f; } template<typename _T> void write( _T x ) { if( x < 0 ){ putchar( '-' ); x = ( ~ x ) + 1; } if( 9 < x ){ write( x / 10 ); } putchar( x % 10 + '0' ); } template<typename _T> _T MIN( const _T a, const _T b ) { return a < b ? a : b; } template<typename _T> _T MAX( const _T a, const _T b ) { return a > b ? a : b; } double pos; struct point { LL x, y; int indx; point(){} point( const LL X, const LL Y, const int Indx ) { x = X, y = Y; indx = Indx; } bool operator < ( const point & other ) const { return x < other.x || ( x == other.x && y < other.y ); } bool operator > ( const point & other ) const { return x > other.x || ( x == other.x && y > other.y ); } point operator - ( const point & other ) const { return point ( x - other.x, y - other.y, 0 ); } }P[MAXN * 2]; struct Vector { LL x, y; Vector(){} Vector( const LL X, const LL Y ) { x = X, y = Y; } Vector( const point p ) { x = p.x, y = p.y; } }; struct segment { point l, r; int indx; double endVal() const { if( l.x == r.x ) return l.y; return l.y + 1.0 * ( r.y - l.y ) * 1.0 * ( pos - l.x ) / ( r.x - l.x ); } bool operator < ( const segment & other ) const { return indx != other.indx && endVal() < other.endVal(); } bool operator == ( const segment & other ) const { return indx == other.indx; } }seg[MAXN]; typedef set<segment> :: iterator iter; set<segment> s; int cnt[MAXN]; int N; LL mul( const Vector & fir, const Vector & sec ) { return fir.x * sec.y - fir.y * sec.x; } int sign( const LL x ) { return ! x ? 0 : ( x < 0 ? -1 : 1 ); } bool chk( const segment x, const segment y ) { Vector xl_yr = Vector( y.r - x.l ), xl_xr = Vector( x.r - x.l ), xl_yl = Vector( y.l - x.l ); LL m1 = mul( xl_xr, xl_yr ), m2 = mul( xl_xr, xl_yl ); LL mu1 = sign( m1 ) * sign( m2 ); //这里转sign是因为直接乘的话会爆long long if( mu1 > 0 ) return false; Vector yl_xr = Vector( x.r - y.l ), yl_yr = Vector( y.l - y.r ), yl_xl = Vector( x.l - y.l ); LL m3 = mul( yl_yr, yl_xr ), m4 = mul( yl_yr, yl_xl ); LL mu2 = sign( m3 ) * sign( m4 ); if( mu2 > 0 ) return false; return true; } int main() { // freopen( "jump.in", "r", stdin ); // freopen( "jump.out", "w", stdout ); point lp, rp; int x1, x2, y1, y2; read( N ); for( int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { read( x1 ), read( y1 ), read( x2 ), read( y2 ); seg[i].indx = i; seg[i].l = point( x1, y1, i ); seg[i].r = point( x2, y2, i ); P[2 * i - 1] = seg[i].l; P[2 * i] = seg[i].r; } sort( P + 1, P + 1 + 2 * N ); int fir, sec, ind; for( int i = 1 ; i <= 2 * N ; i ++ ) { pos = P[i].x; ind = P[i].indx; iter it = s.find( seg[ind] ); if( it != s.end() ) { iter pre = it, succ = it; succ ++; if( pre != s.begin() && succ != s.end() ) { pre--; if( chk( seg[pre->indx], seg[succ->indx] ) ) { fir = pre->indx, sec = succ->indx; break; } } s.erase( it ); } else { it = s.lower_bound( seg[ind] ); if( it != s.end() && chk( seg[it->indx], seg[ind] ) ) { fir = ind, sec = it->indx; break; } if( it != s.begin() ) { it --; if( chk( seg[it->indx], seg[ind] ) ) { fir = ind, sec = it->indx; break; } } s.insert( seg[ind] ); } } if( fir > sec ) fir ^= sec, sec ^= fir, fir ^= sec; int cnt = 0; for( int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { if( i ^ sec && chk( seg[i], seg[sec] ) ) cnt ++; } write( cnt > 1 ? sec : fir ), putchar( '\n' ); return 0; }
- 1
信息
- ID
- 4406
- 时间
- 2000ms
- 内存
- 256MiB
- 难度
- 5
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
