1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

panzhicun
**搬运于
2025-08-24 21:31:51,当前版本为作者最后更新于2019-08-08 19:39:06,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
通法:随机化贪心,并且加上各种优化。 先说计算出从A出发,追赶一个当前位置为B,以速度v移动的小虾所需时间的方法如下。
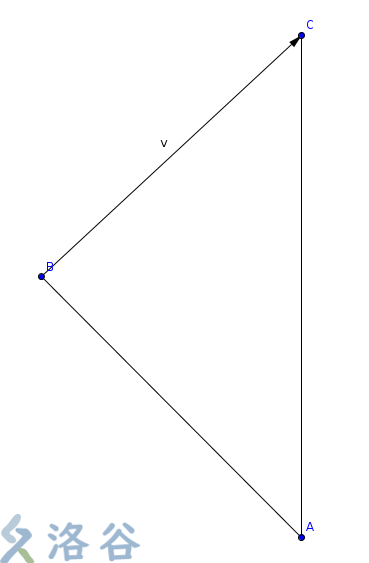
如图所示,根据余弦定理,有:
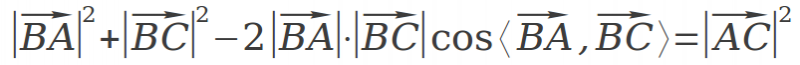
即:
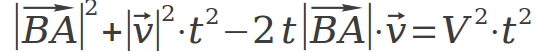
也即:
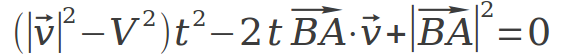
只需要用求根公式求解即可(取两根中的较小正根)。
朴素的随机化贪心算法如下。
先将所有的小虾按体重从小到大排序。
每次将所有小虾按照单位时间的收益(增重比上时间)从大到小排序,选取一个最优的小虾,或者以一定概率接受更差的小虾(并迭代进行,即再以一定概率接受更差的小虾),这个概率可以是0.5,或1/e。
优化1:贪心多次,取最小值;
优化2:对更差的解进行限制(如果太差就直接舍去);
优化3:提高时间所占的比重(按增重比上时间的平方从大到小排序);
优化4:引入模拟退火的思想,即使遇到非常差的解,仍然以一定概率接受它(这个概率跟温度有关,每贪心一次就按照一定规律降温(如将温度减半))。
加上这些优化基本上就可以得全分了。
附程序:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <complex> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const int maxN = 10010; const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198; struct Res { double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {} Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord): t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {} } res[maxN], _res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN]; complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN]; double w[maxN], V, _deltaw, deltaw, T, tem; vector <pair <double, int> > ls; vector <pair <double, int> >::iterator iter; int ord[maxN], n, cnt, _cnt; inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b) {return w[a] < w[b];} inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;} inline double sqr(complex <double> z) {return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));} inline double solve(complex <double> p, complex <double> v, complex <double> O) { double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V), b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)), c = sqr(p - O), delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c; if (delta < -zero) return INF; if (fabs(a) < zero) return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b); double ans = INF, x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a), x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a); if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1; if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2; return ans; } //计算出从O出发,追赶一个当前位置为p,以速度v移动的小虾所需时间。 inline double _rand() {return (double)rand() / RAND_MAX;} inline bool judge() { if (++iter == ls.end()) {--iter; return 0;} if (rand() & 1) {--iter; return 0;} //先以0.5的概率初步淘汰较差的解。 double nxt = iter -> first; --iter; double ths = iter -> first; double delta = (ths - nxt); if (delta / ths < 3.40e-2) return 1; //若较差的解比当前解差3.4%以上,直接淘汰。 return _rand() < 1 / exp(delta / tem); //否则以概率e ^ (-delta / tem)的概率接受更差的解。 } int main() { freopen("nemo10.in", "r", stdin); freopen("nemo10.out", "w", stdout); srand(time(NULL)); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n); complex <double> p0 = p[0]; double w0 = w[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag()); sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp); //将小虾按体重从小到大的顺序排序。 tem = 1; //初始温度设为1。 for (int k = 0; k < 15; ++k) { memset(eaten, 0, sizeof eaten); _deltaw = 0; _cnt = 0; p[0] = p0; w[0] = w0; for (double t = 0; t < T;) { ls.clear(); for (int i = 1; w[ord[i]] < w[0]; ++i) if (!eaten[ord[i]]) ls.push_back(make_pair(w[ord[i]] / sqr(solve(p[ord[i]] + t * v[ord[i]], v[ord[i]], p[0])), ord[i])); sort(ls.begin(), ls.end(), greater <pair <double, int> > ()); iter = ls.begin(); if (iter == ls.end()) break; while (judge()) ++iter; int pos = iter -> second; if (T - (t += solve(p[pos] + t * v[pos], v[pos], p[0])) < -zero) break; _deltaw += w[pos], w[0] += w[pos]; eaten[pos] = 1; _res[_cnt++] = Res(t, p[0] = p[pos] + t * v[pos], pos); } if (_deltaw > deltaw) { deltaw = _deltaw; for (cnt = 0; cnt < _cnt; ++cnt) res[cnt] = _res[cnt]; } //更新最优解。 tem *= .5; } printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord); return 0; }对于不同的数据,还可以用特殊方法求解。
第一组数据显然手算,不多说。
第二组数据较小,可以暴力枚举,附程序:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <complex> using namespace std; const int maxN = 10010; const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198; struct Res { double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {} Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord): t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {} } res[maxN], tmp[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN]; complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN]; double w[maxN], V, deltaw, T; int n, cnt; inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;} inline double sqr(complex <double> z) {return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));} inline double solve(complex <double> p, complex <double> v, complex <double> O) { double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V), b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)), c = sqr(p - O), delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c; if (delta < -zero) return INF; if (fabs(a) < zero) return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b); double ans = INF, x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a), x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a); if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1; if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2; return ans; } void Dfs(int i, double w0, double t, complex <double> p0) { for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; ++j) if (!eaten[j] && w[j] < w0) { double ths = solve(p[j] + t * v[j], v[j], p0); if (t + ths - T > zero) continue; complex <double> pos = p[j] + (t + ths) * v[j]; eaten[j] = 1; tmp[i] = Res(t + ths, pos, j); Dfs(i + 1, w0 + w[j], t + ths, pos); tmp[i] = Res(0, 0, 0); eaten[j] = 0; } if (w0 - w[0] > deltaw) { deltaw = w0 - w[0]; for (cnt = 0; tmp[cnt].t > zero; ++cnt) res[cnt] = tmp[cnt]; } return; } int main() { freopen("nemo2.in", "r", stdin); freopen("nemo2.out", "w", stdout); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n); for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag()); Dfs(0, w[0], 0, p[0]); printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord); return 0; }第三组数据小虾的体重有规律,按顺序吃就是了,附程序:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <complex> using namespace std; const int maxN = 10010; const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198; struct Res { double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {} Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord): t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {} } res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN]; complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN]; double w[maxN], V, deltaw, T; int ord[maxN], n, cnt; inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b) {return w[a] < w[b];} inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;} inline double sqr(complex <double> z) {return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));} inline double solve(complex <double> p, complex <double> v, complex <double> O) { double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V), b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)), c = sqr(p - O), delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c; if (delta < -zero) return INF; if (fabs(a) < zero) return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b); double ans = INF, x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a), x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a); if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1; if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2; return ans; } int main() { freopen("nemo3.in", "r", stdin); freopen("nemo3.out", "w", stdout); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n); for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag()); sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp); for (double t = 0; T - t > zero;) { static int i = 0; ++i; if (i > n) break; double Min = solve(p[ord[i]] + t * v[ord[i]], v[ord[i]], p[0]); int pos = ord[i]; if (fabs(Min - INF) < zero) break; if (T - (t += Min) < -zero) break; w[0] += w[pos]; deltaw += w[pos]; eaten[pos] = 1; res[cnt++] = Res(t, p[0] = p[pos] + t * v[pos], pos); } printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord); return 0; }第四组数据中所有小虾静止不动且在一条直线上,据说是区间动态规划,方法至今未知。
第五、六组数据中所有小虾都在高速向下掉,而Nemo的移动速度很小,可以近似看作Nemo在只能水平移动的情况下去接住小虾来吃。
先将小虾按竖直方向排序,然后进行一下操作。
设f[i]表示前i个小虾中恰好第i个被吃所能得到的最大收益,只需要一个n^2的动态规划即可求解。
附程序:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <complex> using namespace std; const int maxN = 10010; const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198; struct Res { double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {} Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord): t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {} } res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN]; complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN]; double f[maxN], w[maxN], V, deltaw, T; int ord[maxN], g[maxN], n, cnt; inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b) {return imag(p[a]) < imag(p[b]);} void calc(int i) { if (g[i]) calc(g[i]); res[cnt++] = Res(imag(p[i]) / 1000, p[i], i); deltaw += w[i]; return; } int main() { freopen("nemo5.in", "r", stdin); freopen("nemo5.out", "w", stdout); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n); for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag()); sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp); int st = 1; while (imag(p[ord[st]]) / 1000 - real(p[ord[st]]) / V < -zero) ++st; f[ord[st]] = w[ord[st]]; for (int i = 1; i < st; ++i) f[ord[i]] = -INF; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (f[ord[i]] > -INF) for (int j = i + 1; j < n + 1; ++j) { if (imag(p[ord[j]] - p[ord[i]]) / 1000 - fabs(real(p[ord[i]] - p[ord[j]])) / V > -zero) if (f[ord[i]] + w[ord[j]] > f[ord[j]]) f[ord[j]] = f[ord[i]] + w[ord[j]], g[ord[j]] = ord[i]; } int pos = ord[n]; for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) if (f[i] > f[pos]) pos = i; calc(pos); printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), 0., res[i].ord); return 0; }第七、八组数据中可以发现小虾的位置呈现数字三角形的形状,只需要按数字三角形的方法进行动态规划即可。
附程序:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <complex> using namespace std; const int maxN = 2010, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const double zero = 1e-12; struct Res { double t; complex <int> p; int ord; Res() {} Res(double t, complex <int> p, int ord): t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {} } res[maxN], tmp[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN]; complex <int> p[maxN], v[maxN]; double w[maxN], deltaw, V, T, f[maxN][maxN]; int ord[maxN][maxN], g[maxN], n, cnt; inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;} inline double sqr(complex <double> z) {return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));} int main() { freopen("nemo8.in", "r", stdin); freopen("nemo8.out", "w", stdout); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%d%d%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n); for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) scanf("%lf%d%d%d%d", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag()); for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) ord[real(p[i])][imag(p[i])] = i; int i = n; for (; i; --i) { f[real(p[i])][imag(p[i])] = w[i]; if (imag(p[i - 1]) < imag(p[i])) break; } while (--i) { int x = real(p[i]), y = imag(p[i]), ths = ord[x][y]; if (f[x - 1][y + 1] > f[x + 1][y + 1]) { f[x][y] = w[i] + f[x - 1][y + 1]; g[ths] = ord[x - 1][y + 1]; } else { f[x][y] = w[i] + f[x + 1][y + 1]; g[ths] = ord[x + 1][y + 1]; } } double t = 0; res[cnt++] = Res(t = abs(p[1] - p[0]) / V, p[1], 1); for (int ths = 1; g[ths]; ths = g[ths]) res[cnt++] = Res(t += abs(complex <double> (real(p[g[ths]] - p[ths]), imag(p[g[ths]] - p[ths]))) / V, p[g[ths]], g[ths]); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) deltaw += w[res[i].ord]; printf("%d\n%lf\n", cnt, deltaw); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) printf("%.9lf %d %d %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord); return 0; }第九组数据中所有小虾都静止不动,简单的贪心就可以过。
第十组数据可能就只有随机化贪心能够解决了……
- 1
信息
- ID
- 883
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 125MiB
- 难度
- 7
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
