1 条题解
-
0
自动搬运
来自洛谷,原作者为

gghack_Nythix
搬运于
2025-08-24 22:55:23,当前版本为作者最后更新于2024-02-18 20:39:16,作者可能在搬运后再次修改,您可在原文处查看最新版自动搬运只会搬运当前题目点赞数最高的题解,您可前往洛谷题解查看更多
以下是正文
前言:这篇题解是纯暴力,但是居然跑到了最优解前5。
分析:
加强前:
没什么好分析的,你很容易就可以写出下面的代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int a[50005],n,l,r,maxx,ans; int tot[400005]; inline bool ck(int k,int ragez){ for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { if(tot[a[i] % k] == ragez) return 0; tot[a[i] % k] = ragez; } return 1; } signed main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> l >> r; for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { cin >> a[i]; maxx = max(a[i],maxx); if(tot[a[i]] == 1){ cout << 0 ; return 0; } tot[a[i]] = 1; } memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot)); l = max(n,l); if(r > maxx) ans += r - maxx + 1;//计算绝对有解的 int curr = 0; for(register int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k) { ++ curr;if(ck(k,curr)) {++ans;} } cout << ans ; return 0; }在不加强时可以AC,加强后可以通过21个点。
优化:
可以寻找到一部分比当前模数小的数,对这一部分进行标记,表示这些取模后仍然是他本身。容易发现,即使 继续扩大,这一部分依然不用被计算。所以每次直接跳过就可以了
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) using namespace std; int a[50005],n,l,r,maxx,ans,lst,tmp,curr,tot[400005],sqrtsqrt; bool tot2[400005],toto[400005]; inline bool ck(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= n) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= n;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } signed main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> l >> r; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { cin >> a[i]; maxx = max(a[i],maxx); if(toto[a[i]] == 1){ cout << 0; return 0; } toto[a[i]] = 1; } sort(a + 1,a + n + 1); memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot)); l = max(n,l); if(r > maxx) ans += r - maxx + 1; sqrtsqrt = sqrt(n); for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k) { if(ck(k,++curr)) ++ans; } cout << ans ; return 0; }第二次优化:
发现我们可以使用一些原数列本来剩下的值,用这些值去制造一个和他同余的数,如果这个同余的数已经在原序列存在了,那么也就说明冲突了。
如何制造呢?
设 ,其中 就是题面要求的 。 为对 取余的余数。
则 。
也就是说枚举 的多少倍就可以了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define I_love_You() (assert(n <= 11451441)) using namespace std; int a[50005],n,l,r,maxx,ans,lst,tmp,curr,tot[400005],sqrtsqrt; bool tot2[400005],toto[400005]; inline bool ck(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= n) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= n;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } signed main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> l >> r; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { cin >> a[i]; maxx = max(a[i],maxx); if(toto[a[i]] == 1){ cout << 0; return 0; } toto[a[i]] = 1; } sort(a + 1,a + n + 1); memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot)); l = max(n,l); if(r > maxx) ans += r - maxx + 1; sqrtsqrt = sqrt(n); for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k) { if(k >= sqrtsqrt) { for(int i = 1;i <= sqrtsqrt;++i) { for(int j = a[i] + k;j <= a[n];j += k) { if(toto[j]) goto nimade; } } } if(ck(k,++curr)) ++ans; nimade: I_love_You(); } cout << ans ; return 0; }好嘛,差几个点AC。
又叕叕优化:容易发现,如果 ,可以说明在 区间中的数对取模一定是不会冲突的,最坏情况下会剩下 个余数没有被使用。
对于 的选择,自然是选择小于 时,这个数不冲突,消除干扰。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define I_love_You() (assert(n <= 11451441)) using namespace std; int a[50005],n,l,r,maxx,ans,lst,tmp,curr,tot[400005],sqrtsqrt,f[400005]; bool tot2[400005],toto[400005]; inline bool ck(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= n) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= n;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } inline bool cky(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= sqrtsqrt) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= sqrtsqrt;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } signed main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> l >> r; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { cin >> a[i]; maxx = max(a[i],maxx); if(toto[a[i]] == 1){ cout << 0; return 0; } toto[a[i]] = 1; } sort(a + 1,a + n + 1); memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot)); l = max(n,l); if(r > maxx) ans += r - maxx + 1; sqrtsqrt = 0.4376 * sqrt(n); for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k){ while(!cky(k,++curr)) --sqrtsqrt; if(cky(k,++curr)) break; } for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k) { if(k >= sqrtsqrt) { for(int i = 1;i <= sqrtsqrt;++i) { for(int j = a[i] + k;j <= a[n];j += k) { if(toto[j]) goto nimade;//存在同余 } } } if(k > a[n] - a[sqrtsqrt]) {++ans;continue;} if(ck(k,++curr)) ++ans; nimade: I_love_You(); } cout << ans ; return 0; }T掉了最后一个点。
继续优化:
发现这个程序在序列中数字比较连续时容易TLE。那么我们对于这种连续(即)的块一个个做处理。
做处理时,我们不妨换一种思路,不对原数进行显著的放入桶判断模数相等,而是转化成线段覆盖问题:
设当前两个块分别是,,块中的起始,终止元素对 取余的结果为,:
考虑记录这两个块中的起始元素和终止元素,这之中的余数一定不会离散的分布,但注意,他们之间的模数有几率变回0。
- 先考虑两个块不变回0的情况,即的均大于:
此时的线段长这个样子:
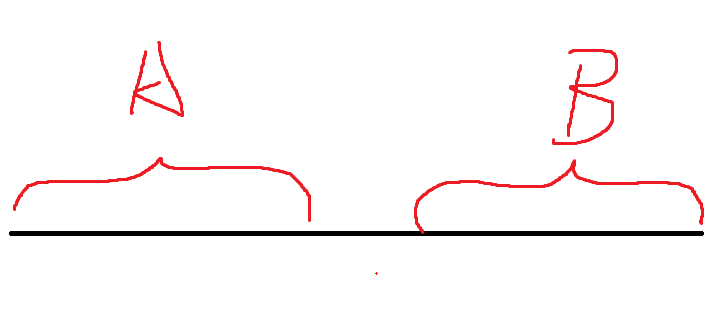
只需要判断两条线段是否相交。
- 其中一个分裂成两条线段:
此时长这个样子:

可以判断另外一套线段是否和空白区相交。
- 两个都分裂了:
此时长这个样子

我是将其中一个线段分成 和 来判断的,当然仔细想想这种情况明显不成立。
讨论完之后就可以愉快的写代码了,时间复杂度应该也是 左右的:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define I_love_You() (assert(n <= 11451441)) using namespace std; int a[50005],n,l,r,maxx,ans,lst,tmp,curr,tot[400005],sqrtsqrt,f[400005],cntt; bool tot2[400005],toto[400005]; struct node{ int len,st,ed; bool operator < (const node & hh) const { return len > hh.len; } }; vector<node> vec; inline bool ck(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= n) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= n;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } inline bool cky(int k,int ragez){ while(a[lst] < k && lst <= sqrtsqrt) ++ lst,tot2[a[lst]] = 1;//这些一定不需要 for(int i = lst;i <= sqrtsqrt;++i) { tmp = a[i] % k; if(tot[tmp] == ragez || tot2[tmp]) return 0; tot[tmp] = ragez; } return 1; } inline int qp(int a,int b){ int ans = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) ans = ans * a; a = a * a; b >>= 1; } return ans; } namespace gghack{ inline bool cka(int k){ for(int i = 0;i < signed(vec.size());++i) {//前面的和当前的比较 for(int j = 0;j < i;++j) {//枚举前面的 if(vec[i].st % k <= vec[i].ed % k){ int lftmd = 0,rgtmd = 0,mode = 0; if(vec[j].st % k > vec[j].ed % k || (vec[j].ed % k - vec[j].st % k + 1) != vec[j].len) {//取模爆掉了成为了0 lftmd = vec[j].ed,rgtmd = vec[j].st;//有剩余格子的就是这一坨 mode = 1;//成为判断是否不在冲突范围中 } else lftmd = vec[j].st,rgtmd = vec[j].ed; if(mode) {//相当于两条断开的线段和一条完整的线段判断线段覆盖 if(!(vec[i].st % k > lftmd && vec[i].ed % k < rgtmd))return 0;//不在空闲的那一坨 } else { if((vec[i].st % k >= lftmd && vec[i].ed % k <= rgtmd) || (vec[i].st % k >= lftmd && vec[i].st % k <= rgtmd) || (vec[i].ed % k <= rgtmd && vec[i].ed % k >= lftmd) || (vec[i].st % k <= lftmd && vec[i].ed % k >= rgtmd))return 0;//不在外面的那一坨白色区域 } } else {//这一波也是拆成两个线段,一个是st ~ k - 1,一个是0 ~ ed int lftmd = 0,rgtmd = 0,mode = 0; if(vec[j].st % k > vec[j].ed % k || (vec[j].ed % k - vec[j].st % k + 1) != vec[j].len) {//取模爆掉了成为了0 lftmd = vec[j].ed,rgtmd = vec[j].st;//有剩余格子的就是这一坨 mode = 1;//成为判断是否不在冲突范围中 } else lftmd = vec[j].st,rgtmd = vec[j].ed; if(mode) {//相当于两条断开的线段和一条完整的线段判断线段覆盖 if(!(vec[i].st % k > lftmd && k < rgtmd))return 0;//不在空闲的那一坨 if(!(0 > lftmd && vec[i].ed % k < rgtmd))return 0;//不在空闲的那一坨 } else { if((vec[i].st % k >= lftmd && k <= rgtmd) || (vec[i].st % k >= lftmd && vec[i].st % k <= rgtmd) || (k - 1 <= rgtmd && k - 1 >= lftmd) || (vec[i].st % k <= lftmd && k - 1 >= rgtmd))return 0;//不在外面的那一坨白色区域 if((0 >= lftmd && vec[i].ed % k <= rgtmd) || (0 >= lftmd && 0 <= rgtmd) || (vec[i].ed % k <= rgtmd && vec[i].ed % k >= lftmd) || (0 <= lftmd && vec[i].ed % k >= rgtmd))return 0;//不在外面的那一坨白色区域 } } } } return 1; } void tohack(){ for(int k = l;k <= min(maxx - 1,r);++k) {if(cka(k))++ans;} cout << ans << '\n'; exit(0); } } signed main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> l >> r; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { cin >> a[i]; maxx = max(a[i],maxx); if(toto[a[i]] == 1){ cout << 0; return 0; } toto[a[i]] = 1; } sort(a + 1,a + n + 1); memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot)); l = max(n,l); if(r > maxx) ans += r - maxx + 1; sqrtsqrt = sqrt(n);//玄学调参 for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k){ while(!cky(k,++curr)) --sqrtsqrt;//余数冲突满足单调性 if(cky(k,++curr)) break;//这个都符合了,下一个更大的余数会被映射到更大的空间,可以跳过 } int d = 1; for(int i = 2;i <= n + 1;++i) { if(a[i - 1] + 1 != a[i]){ vec.emplace_back(node{d,a[i - d],a[i - 1]}); d = 1; ++i; } ++d; } if(vec.size() >= 2 && vec.size() <= sqrt(sqrt(n))){gghack::tohack();return 0;} for(int k = l;k <= min(r,maxx - 1);++k) { if(k >= sqrtsqrt) { for(int i = 1;i <= sqrtsqrt;++i) { for(int j = a[i] + k;j <= a[n];j += k) { if(toto[j]) goto nimade;//存在同余 } } } if(k > a[n] - a[sqrtsqrt]) {++ans;continue;} if(ck(k,++curr)) ++ans; nimade: I_love_You(); } cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }后记:

卡不掉应该也差不多了吧,毕竟只要解决题目都可以。
- 1
信息
- ID
- 9806
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 512MiB
- 难度
- 5
- 标签
- 递交数
- 0
- 已通过
- 0
- 上传者
